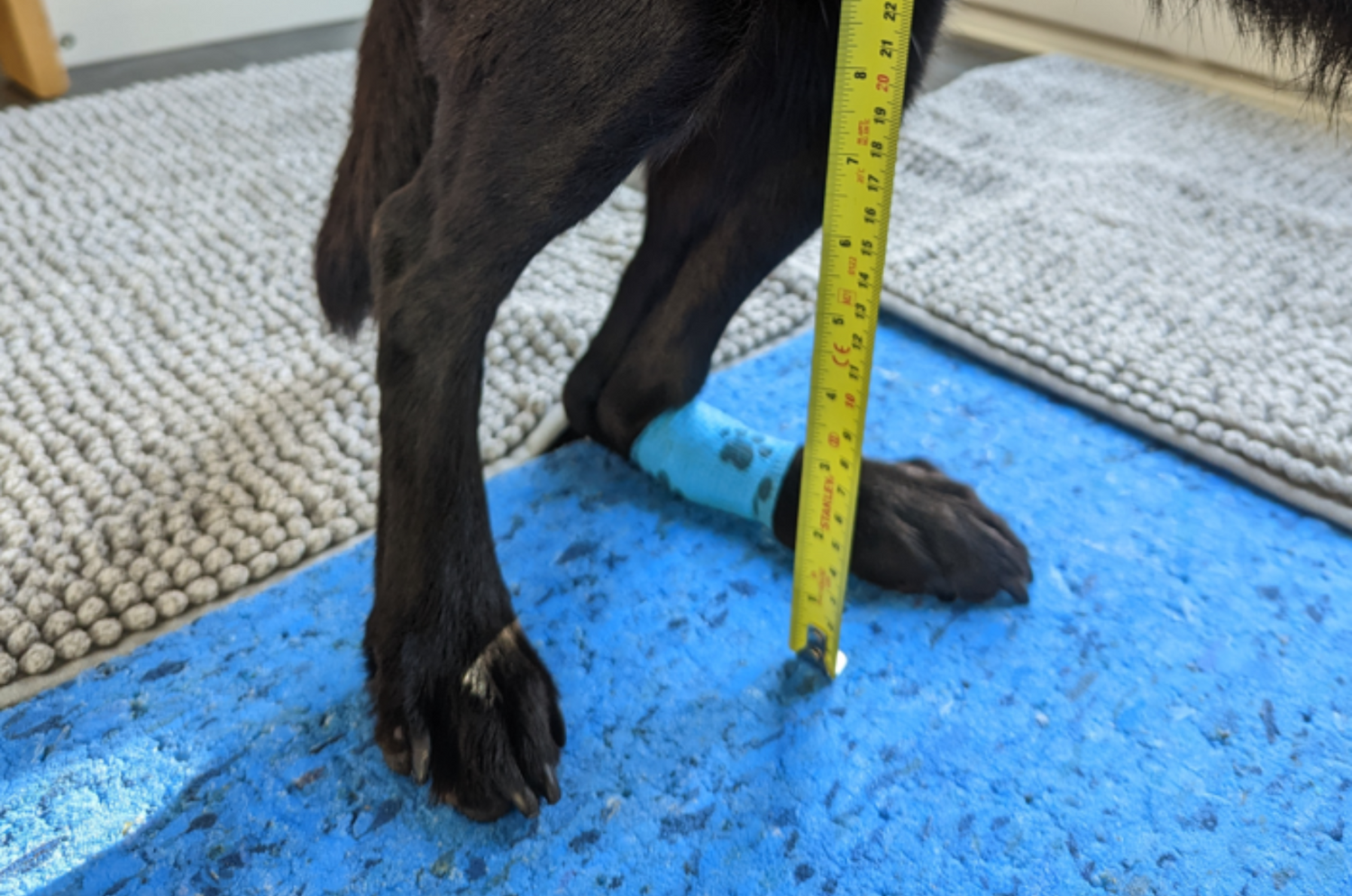
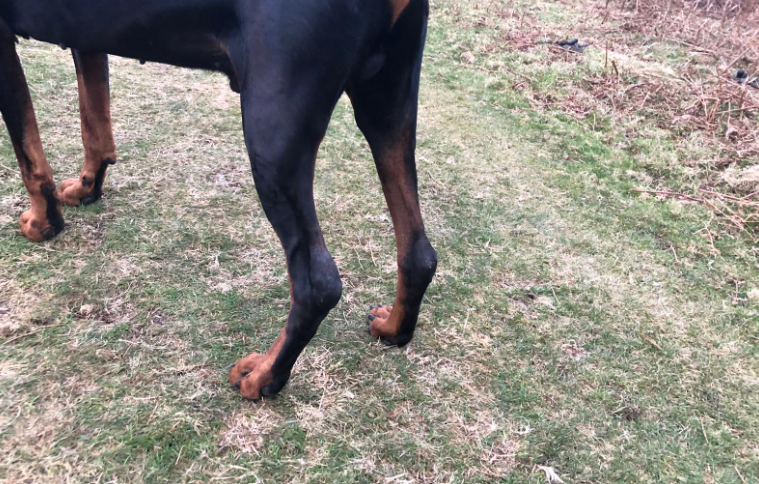
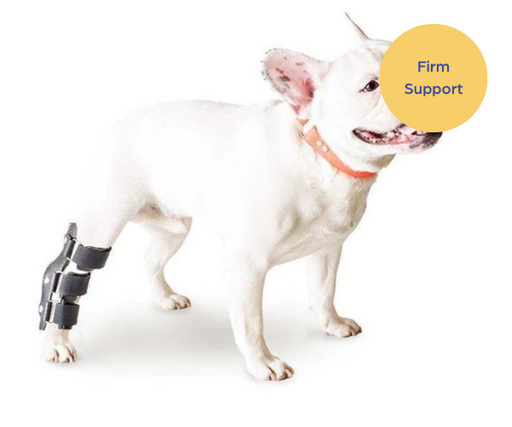
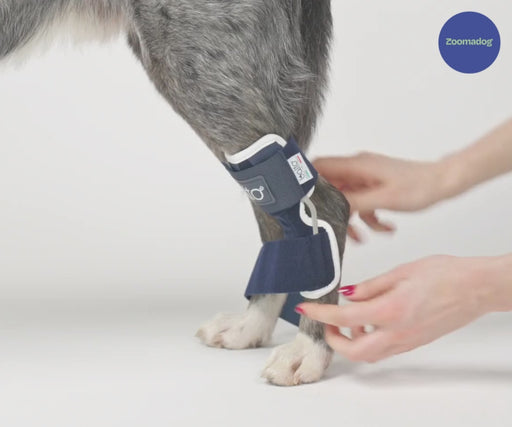
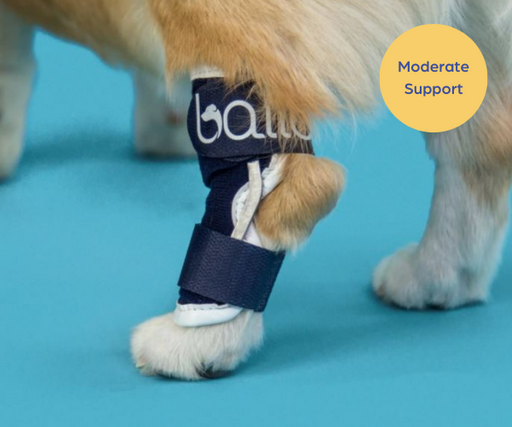
What is an Achilles Tendon Injury?
An Achilles Tendon injury is when the tendon is bruised, pulled or torn / ruptured.
Grade 1 - Mild - bruising
Grade 2 - Moderate - partial tendon tear
Grade 3 - Severe - complete disruption/tear of tendon fibers, there’s a complete lack of tension on the tendon when the hock is flexed (plantigrade stance)
The Achilles Tendon (or the common calcaneal tendon) is a large band of fibrous tissue, that connects the calf muscles to the heel bone on your dog’s hind leg, it involves five different muscles.
The Achilles Tendon plays a crucial role in allowing the extension of the hind leg, facilitating running, jumping and other every day activities of your dog. These injuries are very painful, and often your dog will not want to walk far or leave the house.